Business Sectors
Events
Floating energy: successfully unlocking stranded gas using FLNGs and FSRUs
Contents
Register to read more articles.
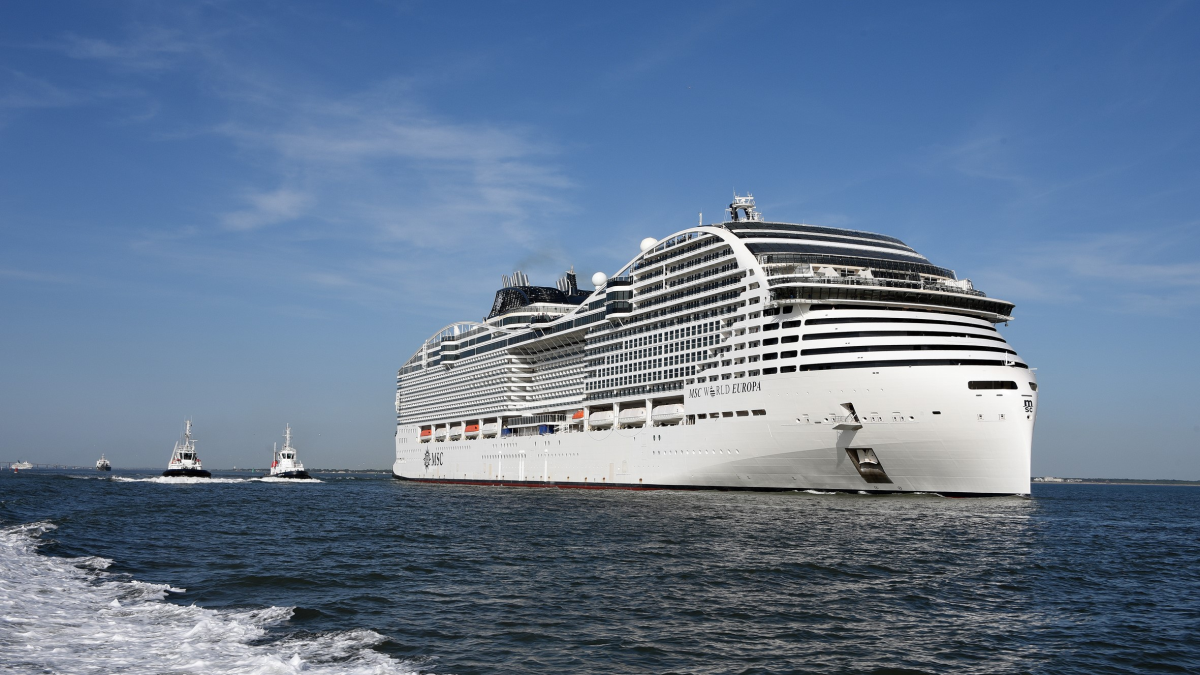
Cruise ships and clean(er) fuel
LNG provides a cleaner fuel option for cruise ships, allowing compliance with IMO emissions regulations, and a more pleasant experience for passengers, writes Small Scale LNG principal, Eduardo Perez Orue
Cruise shipping is bouncing back; after a disastrous period where most ships remained idle for months during the Covid-19 pandemic, the public is coming back in hordes. Most shipping companies are returning to profitability and a rosy future, with maybe only one concern on the horizon: emissions from burning fossil fuels. Passengers are demanding more environmentally friendly ships, not only because they are aware of the current climate emergency but also because they have had the unpleasant experience of breathing in the fumes of a fuel oil-burning engine while on deck. I have been there myself, and I can assure you that the prospect of a cruise free of fumes is alluring.
“LNG helps cruise ships comply with stringent environmental regulations”
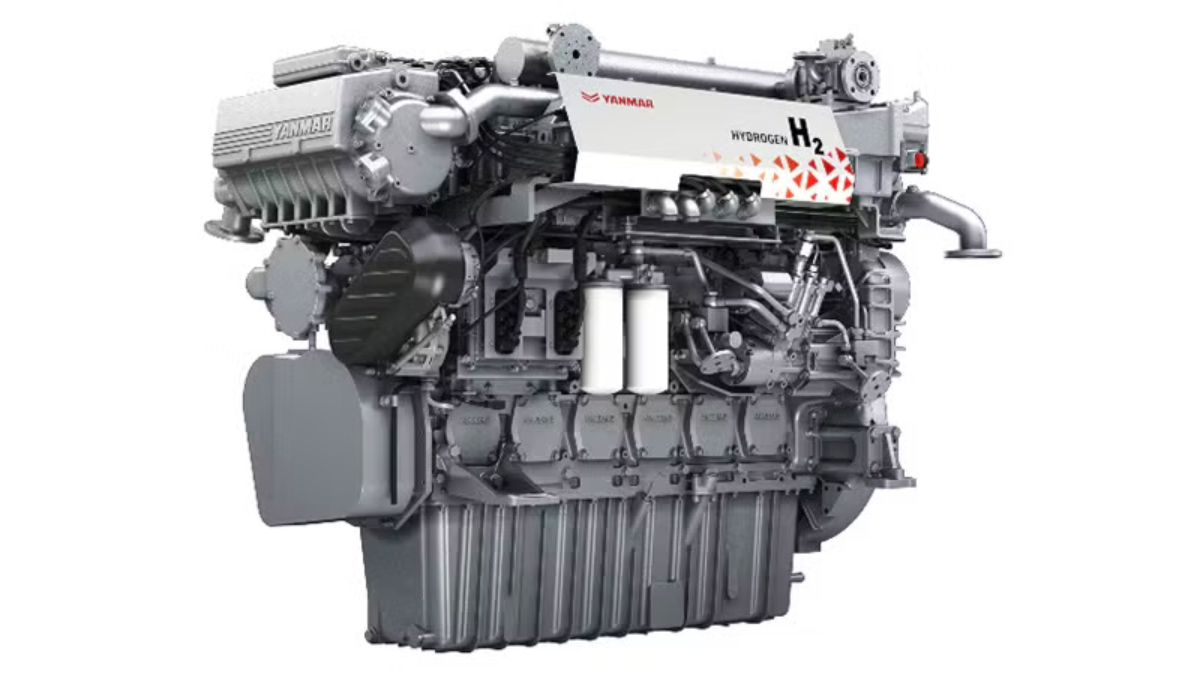
So, what alternatives do cruise shipowners have? In the short term, only LNG as fuel. All other alternative fuels are not yet a real solution.
Although LNG as a fuel has many advantages for cruise ships, the switch will not be without problems. Let’s look at some pros and cons of using LNG in cruise ships.
The pros
Lower emissions: LNG is considered a cleaner-burning fuel compared to traditional marine fuels, such as heavy fuel oil. It produces fewer greenhouse gas emissions, sulphur oxides (SOx), and particulate matter, contributing to improved air quality and reduced environmental impact. This is especially important in cruise ships that are visiting nature sites and where the passengers might give a special consideration to lower or no emissions.
Regulatory compliance: LNG helps cruise ships comply with stringent environmental regulations, such as the IMO’s sulphur cap regulations, which limit the sulphur content in marine fuels.
Reduced noise levels: LNG-powered engines generally produce lower noise levels compared to traditional engines, contributing to a quieter and more pleasant experience for passengers.
The cons
Capex costs: retrofitting or building new cruise ships to run on LNG can involve significant upfront costs. Additionally, the development of LNG infrastructure at ports, including bunkering facilities, can be expensive.
Limited bunkering infrastructure: there are about 165 LNG facilities and bunker vessels in operation globally, according to DNV Alternative Fuels Insight.
Methane slip: LNG combustion engines produce methane slip, which is the release of unburned methane into the atmosphere, a powerful global warming gas.
Flammability and safety concerns: LNG is highly flammable, and safety measures must be in place to handle and store it securely. The potential for accidents or leaks requires strict safety protocols and specialised training for crew members.
Transition period: the transition from traditional fuels to LNG involves a learning curve for crew members, maintenance staff, and port facilities. Training and adaptation to new technologies may be necessary.
The adoption of LNG in cruises comes with both environmental benefits and challenges. As technology advances and infrastructure improves, the industry may find ways to address some of the current limitations associated with LNG use. Several cruise ship companies have started moving in that direction (Carnival, Disney, Royal Caribbean, MSC and others). In total, there are 20 LNG-fuelled cruise ships operating and another 23 on order or under construction.
Related to this Story
CIC finds ballast water systems driving detentions
Events
Maritime Regulations Webinar Week
Floating energy: successfully unlocking stranded gas using FLNGs and FSRUs
© 2024 Riviera Maritime Media Ltd.