Business Sectors
Contents
Register to read more articles.
Innovations propelling LNG carrier advancements
Recent developments in LNG carrier design enhance efficiency and environmental performance, addressing industry demands for flexibility and sustainability
The liquefied natural gas (LNG) shipping industry is witnessing a transformative phase, marked by innovations in vessel design and technology. These advancements aim to improve operational efficiency, reduce environmental impact, and meet the evolving demands of global energy transport, according to a recent Bureau Veritas (BV) webinar The LNG Value Chain: how far will it grow?, held on 12 February 2025.
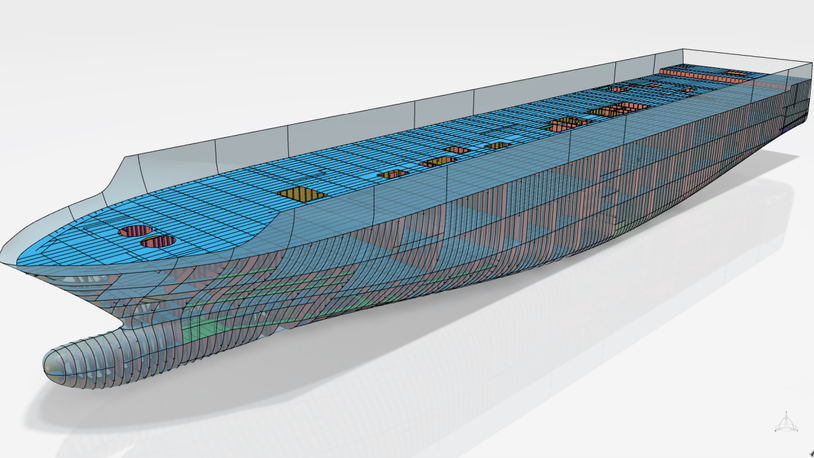
Notable developments highlighted included the three-tank LNG carrier concept by Gaztransport & Technigaz (GTT), which has already received approval in principle from Bureau Veritas.
This design reduces the number of cargo tanks from four to three, maintaining a total capacity of 174,000 m3. The reduction in tank numbers leads to decreased boil-off gas rates and optimised construction and operational costs. GTT has investigated the effect of increased tank length to address the challenges of this new concept.
In parallel, advancements in propulsion systems are contributing to enhanced fuel efficiency.
BV noted the industry has seen a shift from steam turbine propulsion to dual-fuel diesel-electric systems, and more recently to two-stroke dual-fuel engines. These modern engines offer greater propulsive efficiency and fuel flexibility, allowing vessels to optimise operational costs and reduce emissions.
Bureau Veritas global market leader for gas carriers Carlos Guerrero highlighted this trend, "We are looking at new concepts that propose gas turbines or internal combustion engines using spark ignition, as they may offer better performance in terms of methane slip. Some of these new technologies are designed to reduce engineroom volume while increasing cargo capacity, enhancing both efficiency and environmental performance."
Reliquefaction technology has also evolved, with companies developing systems that enable the reliquefaction of boil-off gas. This capability allows LNG carriers to arrive at their destinations with minimal cargo loss, providing greater operational flexibility and economic benefits.
Furthermore, the industry is exploring the integration of alternative fuels to future-proof vessels.
BV noted GTT has secured approvals in principle for its Mark III containment system conversion to use either ammonia or methanol fuels. This adaptability ensures shipowners can navigate the uncertainty of the industry’s transition to greener energy sources while maintaining operational efficiency, noted BV.
Sign up for Riviera’s series of technical and operational webinars and conferences:
- Register to attend by visiting our events page.
- Watch recordings from all of our webinars in the webinar library.
Related to this Story
Events
Offshore Support Journal Conference, Middle East 2025
Maritime Regulations Webinar Week
© 2024 Riviera Maritime Media Ltd.