Business Sectors
Contents
Register to read more articles.
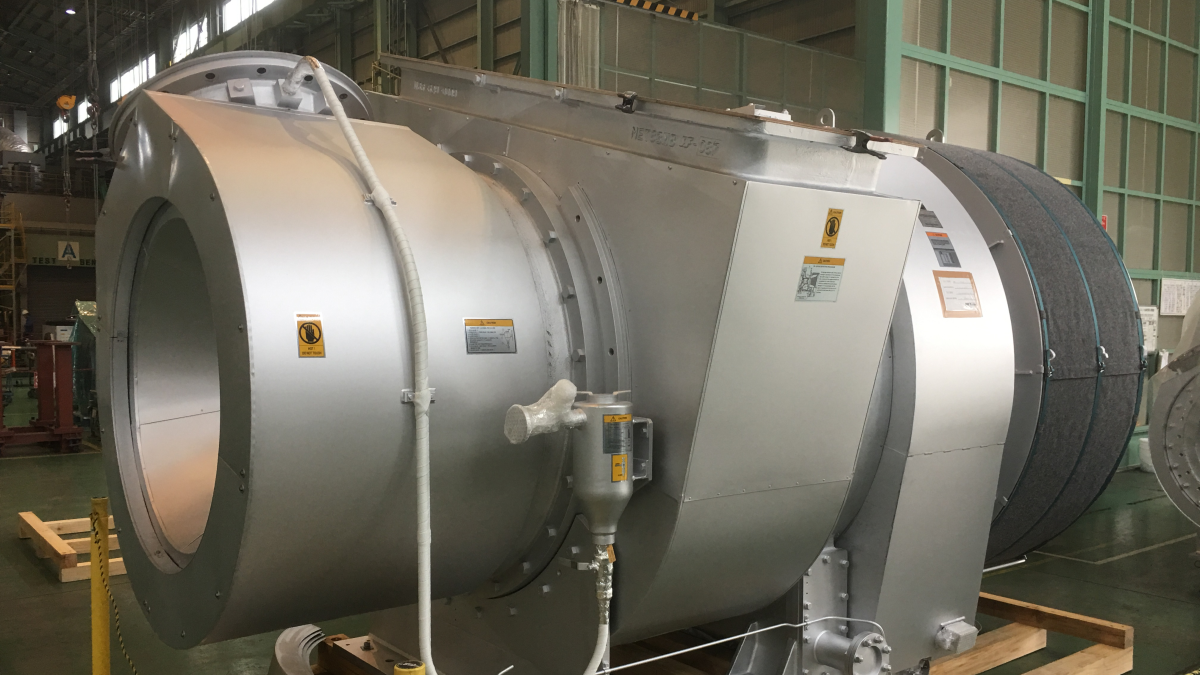
MET turbochargers to be built in China, following licensing deal
Starting 2025, Jiangsu Masada will manufacture the popular axial-flow marine turbochargers in China, following a licensing deal with MHI-MME
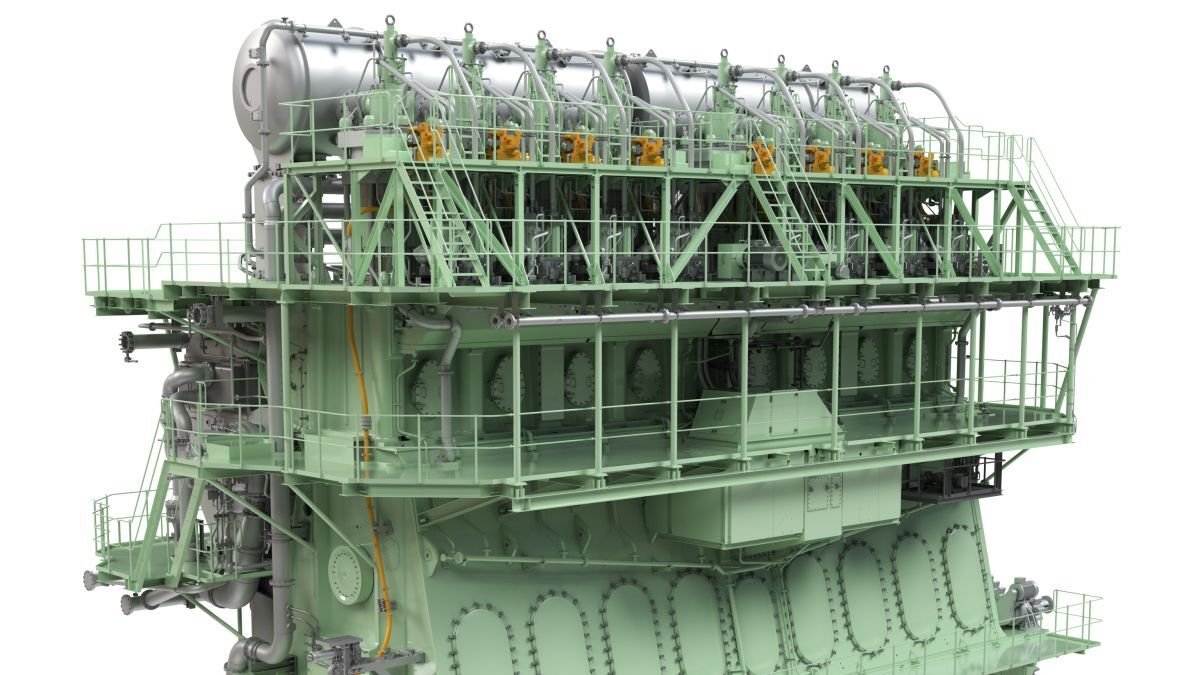
Starting 2025, China’s Jiangsu Masada Heavy Industries will begin the manufacture and sale of MET Turbochargers, under a license agreement inked with Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Marine and Equipment (MHI-MME).
Under the agreement with the Japanese marine equipment manufacturer struck in 2024, Jiangsu Masada will begin assembling and gradually expand to full-scale production of the exhaust gas turbine-type turbochargers for two-stroke marine engines.
Through the licensing agreement, MHI-MME wants to make further inroads into the growing Chinese shipbuilding market. As of Q4 2024, Chinese shipbuilders had secured about 70% of the global newbuild orders based on CGT, according to Clarksons.
Among those in attendance at a ceremony marking the licensing agreement was MHI-MME president and chief executive, Katsuhide Matsunaga. Mr Matsunaga noted the importance of the Chinese market for the group’s long-term growth strategy and highlighted the company’s commitment to helping shipping achieve net-zero greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by 2050. This will require the introduction of new two- and four-stroke dual-fuel engine technology that is capable of combusting low- and zero-carbon fuels, including LNG, methanol, hydrogen and ammonia.
Founded in 2005 in Chongchuan, Nantong City, and privately held, Jiangsu Masada has a long relationship with MHI Group. It holds exclusive licensing agreements with MHI-MME to manufacture deck cranes, steering gears and deck machinery.
“MHI-MME wants to make further inroads into the growing Chinese shipbuilding market”
The new agreement will allow it to manufacture and sell a well-established turbocharger product line.
Non-cooled MET Turbocharger technology was first introduced in 1965, with new series introduced over the years to meet the evolving requirements of marine engine manufacturers. MET turbochargers can be roughly divided into two series: MET-SD, SE, SEII, MA, MB, and MBII series, which are axial-flow turbine turbochargers mainly applied to two-stroke engines; and the MET-SR, SRII, and SRC series, which are radial turbine turbochargers mainly applied to four-stroke engines.
In 2020, MHI-MME improved its axial-flow turbine turbocharger MET-MB series to release the MET-MBII series. The new casing of the MET-MBII is longer in the axial direction to allow greater design freedom, resulting in an optimised flow path compared to conventional casings, according to the manufacturer. This and other design changes have resulted in improved overall turbocharger efficiency by approximately 0.5 to 1.0%, according to a technical paper presented by MHI at CIMAC 2023 in Busan.
By adopting a new shaped gas inlet casing for the MET-MBII, MHI-MME was able to increase airflow capacity by 16% to improve efficiency.
The Japanese marine manufacturer has been evolving its MET turbochargers to meet the needs of the increasing number of high-pressure and low-pressure engines for selective catalytic reduction (SCR) and exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) tuning and can be applied to both MAN Energy Solutions and WinGD dual-fuel engines.
Furthermore, the benefit of sequential turbocharging is that it concentrates what little exhaust gas is available at low engine speeds to one of the turbochargers. When there is a large amount of exhaust gas, the gas is directed to both turbochargers, or just the larger of the two units, to optimise turbocharging over a broader range of engine speeds.
Related to this Story
Events
Maritime Decarbonisation, Europe: Conference, Awards & Exhibition 2025
Offshore Support Journal Conference, Americas 2025
LNG Shipping & Terminals Conference 2025
© 2024 Riviera Maritime Media Ltd.