Business Sectors
Events
Floating energy: successfully unlocking stranded gas using FLNGs and FSRUs
Contents
Register to read more articles.
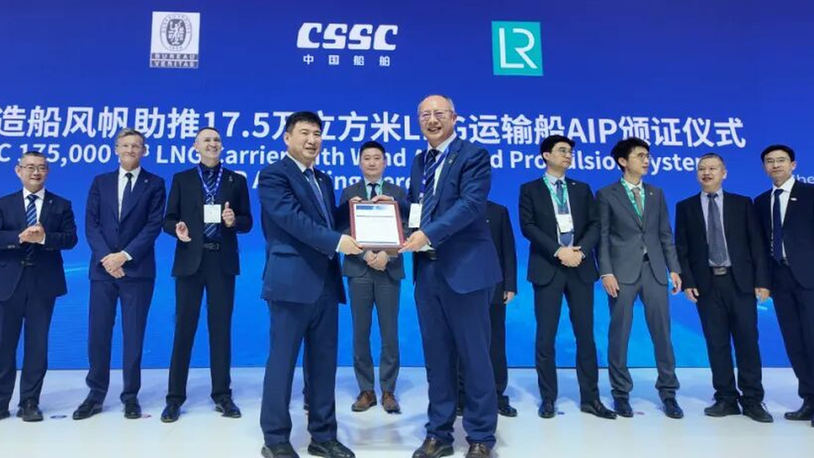
Wind-assisted LNG carrier concept gains class AiP
A wind-assisted LNG carrier concept has been awarded class approval in principle, one of several AiPs granted in the LNG sector
Bureau Veritas has granted an approval in principle (AiP) for a wind-assisted LNG carrier concept developed by Dalian Shipbuilding Industry Co (DSIC), part of an ongoing process of innovations in the LNG sector active through 2025.
Bureau Veritas said the concept incorporated four foldable wing sails, each “providing a maximum thrust of 2,900 kN”, with “a reduction of 5% in energy consumption compared to the same LNG carrier without sails.”
It added aerodynamic performance has been optimised using computational fluid dynamics, alongside “safety and stability analysis”, with the vessel’s hull form and cargo tanks assessed to meet “the International Code for the Construction and Equipment of Ships Carrying Liquefied Gases in Bulk (IGC Code) rules and regulations.”
DSIC noted that the AiP is evidence its wind-assisted approach had progressed beyond a concept sketch, “This groundbreaking achievement confirms the innovation, feasibility and safety of this design solution for LNG carriers,” the yard said, adding it had “a strong foundation for promoting green, low-carbon shipping.”
Bureau Veritas took a similar line on the maturity of the package, stating, “The endorsement confirms the maturity of this concept and paves the way for further developments and potential future installations of wing sails on LNG carriers.”
Throughout 2025, AiPs were issued in relatively high numbers, reflecting the landscape of innovation in the LNG sector, including another wind-assisted propulsion design announced by Mitsui OSK Lines (MOL) in September 2025.
This updated two updated LNG carrier designs developed with Hyundai Heavy Industries and Samsung Heavy Industries, each incorporating four hard-sail units.
Lloyd’s Register granted AiPs for both designs, and quoted MOL’s expectation that fuel-saving performance “is expected to reach up to approximately 30% per voyage with an average annual saving of 15%-20%,” based on preliminary calculations.
Clarksons’ November 2025 Approvals in Principle Update placed these announcements within a wider surge in design-stage approvals and defines an AiP as “an independent assessment of a vessel design, led by a class society, to confirm its feasibility”, with “the safety, functionality and any potential restrictions on the design” reviewed.
Clarksons also cautioned that an AiP “may never go on to receive type approval, and may never actually be the design used for an actual newbuild order.”
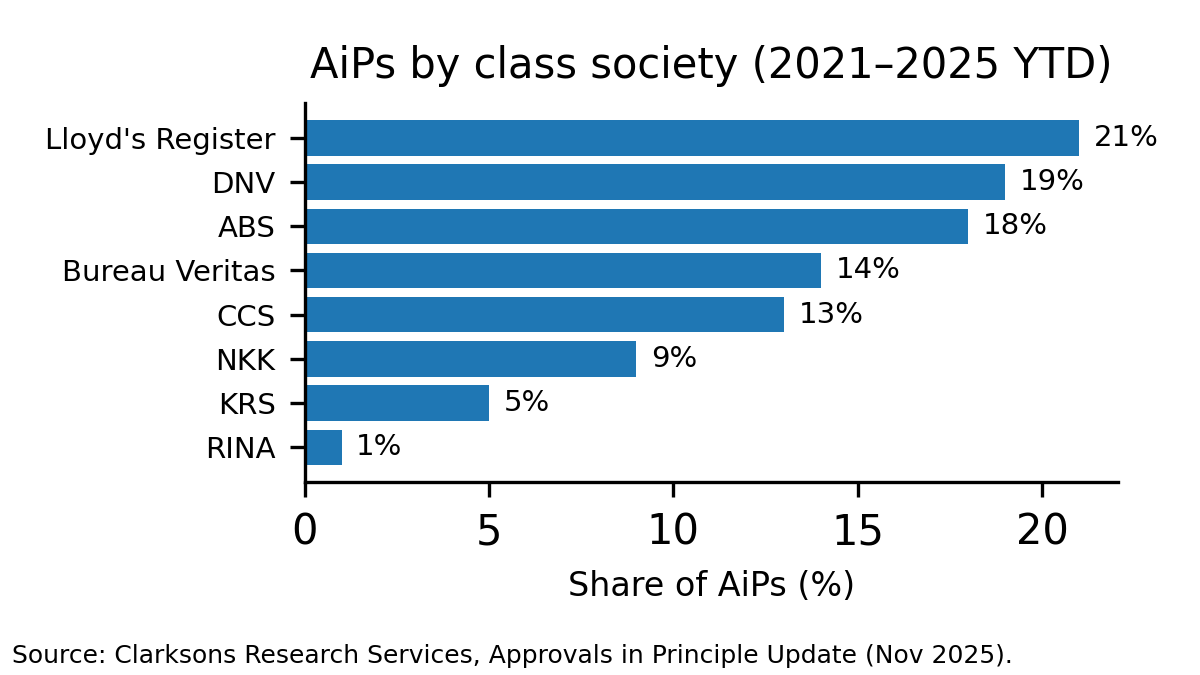
On volume, Clarksons tracked 120 AiPs announced in 2024 and 81 AiPs in 2025 year-to-date, with 340 AiPs announced since the start of 2021.
It also showed LNG as a major fuel strand across AiPs, alongside ammonia and other alternative fuel pathways.
Clarksons’ breakdown by class society attributed 21% of 2021–2025 year-to-date AiP designs to Lloyd’s Register, 19% to DNV, 18% to ABS, and 14% to Bureau Veritas.
Riviera’s LNG Shipping & Terminals Conference will be held on 10-11 November 2026. Use this link for more information and to register for the event.
Related to this Story
NZF delay: what next for IMO’s headline policy?
Events
Maritime Regulations Webinar Week
Floating energy: successfully unlocking stranded gas using FLNGs and FSRUs
© 2024 Riviera Maritime Media Ltd.